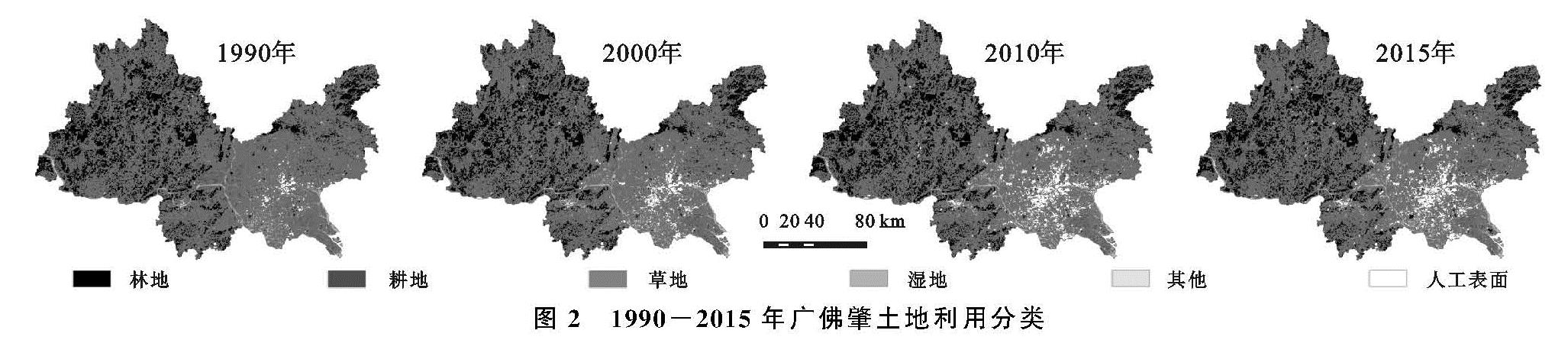
(1)研究区在1990—2015年,林地和耕地面积持续减少,人工表面用地面积逐渐增加,草地先减少后增加,湿地先增加后减少,其他用地呈现出先缓慢增加后急速下降最后又急速上升的变化趋势。25 a间,人工表面的动态度最大,其次是其他用地。耕地的转出量最大,主要转换成人工表面、湿地和林地; 人工表面转入的面积最多,25 a间共转入了1 437.45 km2,主要转入来源是耕地,其次是林地。经济的发展和城镇化进程的推进不应以破坏林地和耕地为前提,广佛肇应加强对林地和耕地的保护,严格控制人工表面的扩张,确保土地利用向可持续性方向发展。
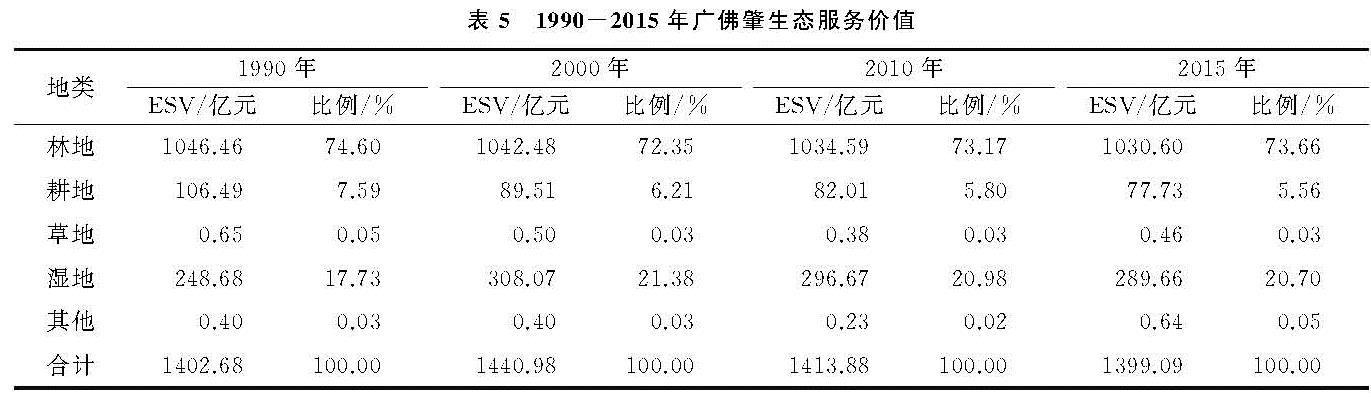
(2)广佛肇在1990—2015年,土地利用的生态系统服务价值总体上呈现出先增加后逐年减少的趋势,25 a间共减少了3.59亿元。林地和耕地的生态服务价值持续减少,湿地的生态价值呈现出先增加后减少的趋势。林地和湿地的生态价值在研究区生态系服务总价值中占据突出地位,林地和耕地面积的减少是广佛肇生态服务价值减少的主要原因; 从单项服务价值排序可以看出,广佛肇调节功能和支持功能生态服价值远大于供给功能和文化功能服务价值之和。耕地面积的下降使保持土壤的服务价值下降最明显。土地利用变化带来的生态系统服务价值减少问题,值得引起当地政府的重视。
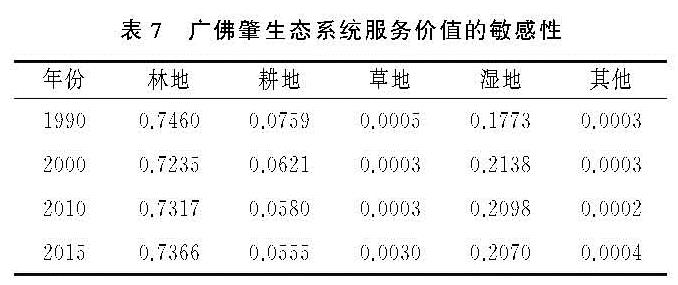
(3)广佛肇在不同时期不同土地利用类型的敏感性系数均小于1,说明广佛肇整体的生态服务总价值对其生态服务价值系数缺乏弹性,经过修正的生态服务价值系数适用于广佛肇。敏感性指数值由大到小排序依次为林地>湿地>耕地>草地>其他,研究期间林地对广佛肇生态系统服务价值的贡献率最大。
本文在研究广佛肇整体的生态系统服务价值时,没有考虑人工表面的生态价值计算,而人工表面主要包括工矿用地、交通用地、居民地等,它对水文调节等单项功能会产生一定的负面效益,但有关人工表面的生态服务价值计算目前研究评价方法不一,因此关于人工表面的生态服务价值核算将是下一步的研究重点。生态系统服务价值受多种因素的影响,本研究虽然对生态系统服务功能评价的方法进行了局部修正,得出的结果具有一定的参考价值。但修正时考虑的因素较少,会对最后的分析结果造成一定的影响,后续将会考虑其他影响生态系统服务价值的因素,以便使估算结果更加准确。