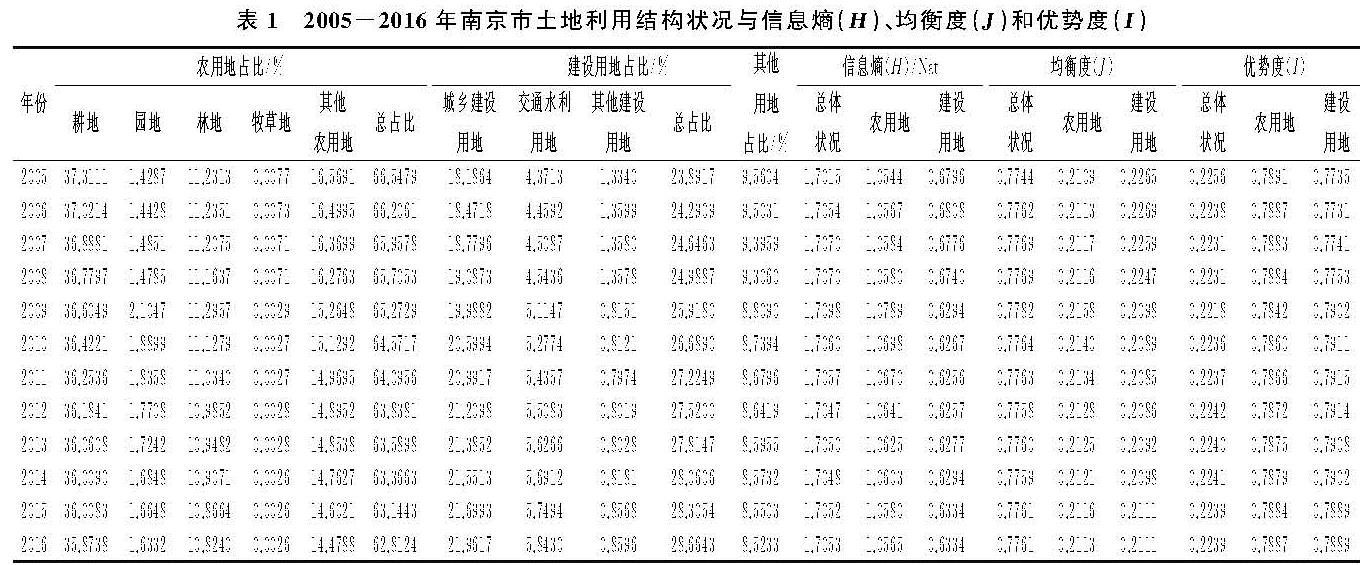
2.2.1 不同地类空间差异特征
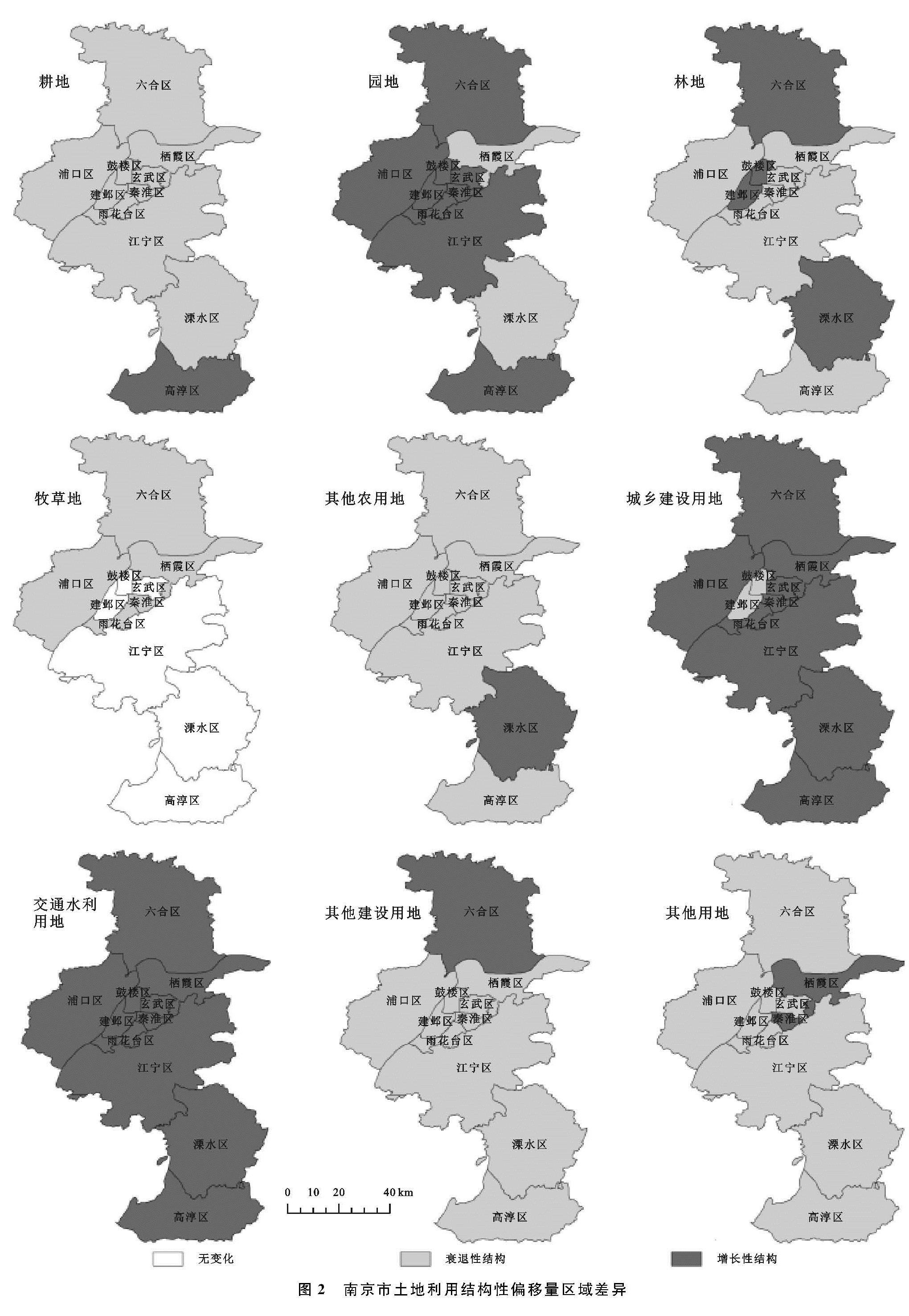
基于SSM模型得出2005—2016年南京市土地利用结构性偏移量,运用ArcGIS 10.3软件绘制出不同地类空间差异图(图2)。由图2可知,研究期内南京市各区各地类结构偏移量演变特征差异显著。
(1)农用地方面,耕地的结构性偏移量除高淳为正值外,其余各区均为负值,属于衰减性结构,表明占用耕地进行区域建设的情况有所改善; 园地的结构性偏移量除栖霞和溧水为负值外,其余各区均为正值,表明园地增长率超过了全市用地增长率,属于增长性结构; 林地的结构性偏移量中,玄武、秦淮、浦口、栖霞、雨花台、江宁和高淳为负值,其余各区为正值,表明前者属于衰减性结构,后者属于增长性结构; 牧草地的结构性偏移量除玄武、建邺、鼓楼、江宁、溧水和高淳由于无牧草地处于不变状态之外,其余各区均为负值,表明牧草地在全市用地的比重中有所减少,属于衰减性结构; 其他农用地的结构性偏移量除溧水区为正值外,其余各区均为负值,基本上属于衰减性结构。
表1 2005-2016年南京市土地利用结构状况与信息熵(H)、均衡度(J)和优势度(I)
(2)建设用地方面,城乡建设用地的结构性偏移量除建邺和鼓楼为负值外,其余各区均为正值,表明城乡建设用地增长率超过全市用地增长率,属于增长性结构; 交通水利用地的结构性偏移量均为正值,表明其增长率超过了全市用地增长率,属于增长性结构; 其他建设用地除六合为正值外,其余各区均为负值,属于衰退性结构,表明其在全市土地利用中的比重越来越小,该类用地对区域经济增长的推动作用减弱。
(3)其他用地方面,除玄武的结构性偏移量为正值外,其余各区其他用地结构性偏移量均为负值,属于衰减性结构,表明各区其他用地在南京市土地利用结构中比重逐年减小。
总体上看,2005—2016年南京市土地利用结构性偏移量中耕地、林地、牧草地、其他农用地、其他建设用地和其他用地为负值,属于衰退性结构,而园地、城乡建设用地和交通水利用地均为正值,属于增长性结构。不难看出,研究年限内南京市建设用地结构性增长需求大于农用地结构增长需求,对区域经济增长贡献较大,表现为大量农用地结构类型面积逐年减少,转移为区域经济建设需求性与服务性用地,使得建设用地面积逐年增加,这是由于南京市社会经济快速发展,导致城市建设扩张、产业布局用地刚性需求增加占用农用地,以满足经济建设需求。
2.2.2 不同片区空间分异特征
根据区域土地利用特点以及社会经济阶段性特征,并结合南京市空间发展战略规划,把南京市11个区划分为“四大片区”(图1)。同时,依据南京市土地利用结构竞争偏移分量值,借助SPSS 22软件运用系统聚类法和平方Euclidean距离对南京市各区状况开展聚类分析,把南京市各区土地利用结构的竞争偏移分量大致划分为四大类别值区,由高到低分别为高值区、中高值区、中值区、低值区,并运用ArcGIS 10.3软件绘制出南京市土地利用结构竞争偏移分量的空间分异图(图3)。
(1)主城区。主城区竞争偏移分量表现为玄武区各地类均为低值区; 秦淮区耕地、园地、牧草地、其他农用地、城乡建设用地和其他建设用地为中值区,林地、交通水利用地和其他土地为低值区; 雨花台区耕地、林地、牧草地、其他农用地和其他建设用地为高值区,园地、城乡建设用地、交通水利用地和其他用地为中高值区; 建邺区耕地、园地、其他农用地、其他建设用地为中高值区,林地、牧草地、城乡建设用地、交通水利用地和其他用地为中值区; 鼓楼区耕地和其他建设用地为高值区,园地、其他农用地、城乡建设用地为中高值区,林地、牧草地、交通水利用地和其他用地为中值区。据此,主城区土地利用结构竞争偏移分量为中值区—低值区状态。随着区域社会经济发展水平不断提高,主城区各地类新增用地吸纳作用逐渐减弱,这是由于主城区是区域社会经济集聚中心,土地资源极为有限,发展空间趋于饱和,地方政府通过强化区域土地用途管制与空间布局结构规划以推进土地集约节约利用“双提升”战略实施,通过旧城改造、低效用地再开发等措施着力提高土地利用效率,同时实施建设用地增减挂钩、土地综合整治等,在一定程度上遏制了各地类用地增长驱动力。
(2)江北新区。江北新区竞争偏移分量表现为六合区除了园地和其他农用地为中高值区外,其他地类均为高值区; 浦口区耕地、其他农用地和其他建设用地为高值区,园地、林地、牧草地和其他用地为中高值区,交通水利用地为中值区。整体上,江北新区土地利用结构竞争偏移分量为中高值区—高值区状态,表明该区域各类用地结构的新增用地类型均有显著的汇集,特别是2015年正式批为国家级新区后,招商引资政策与人才政策使得各类基础设施建设与区域功能性完善对建设用地需求日趋增大,使得土地向工业用地、公共设施用地等倾斜。然而,各项建设扩张不可避免的侵占农用地,特别是耕地占用。因此,严格实施耕地和基本农田保护政策,强化耕地占补平衡,着力推进农村土地综合整治和工矿用地治理,使得建设用地需求增加的同时有效地保护了农用地数量不减少。但由于江北新区快速发展对建设用地需求较大,这必然导致耕地占用速度大于耕地补充速度,耕地仍处于劣势状态。
(3)近郊区。近郊区竞争偏移分量表现为栖霞区除了园地、城乡建设用地和其他用地为中高值区以及交通水利用地为中值区外,耕地、林地、牧草地、其他农用地、其他建设用地均为高值区。据此,近郊区土地利用结构竞争偏移分量为中高值区—高值区状态。这与江北新区大致相同,以主城区为依托,是城乡经济发展紧密联系的重要地段,既受到城市要素扩散影响,又在一定程度上保留了农村土地利用格局。按配套功能划分,近郊区通常是城镇重点发展和工业集中发展区,是解决城市病、疏散人口、缓解交通用地压力的首选地。在地方政府扶持以及工业发展的背景下,使得各项服务性用地需求逐渐增大,通常呈现出低密度蔓延式扩展态势。
(4)远郊区。远郊区竞争偏移分量除园地为中高值区外,耕地、林地、牧草地、其他农用地、城乡建设用地、交通水利用地、其他建设用地和其他用地均为高值区。总体上,远郊区土地利用结构竞争偏移分量为高值区。为响应南京市区域整体发展和城乡一体化发展要求,2013年对高淳、溧水撤县建区,自此两区发生了一系列变化。一方面,受区域经济建设辐射带动效应影响,远郊区作为后备经济发展拓展保障区,招商引资出现井喷,一批高端现代服务业项目、新兴产业项目落户,交通道路、基础设施等建设使得建设用地竞争力较强。另一方面,远郊区兼具农业生产性功能,积极调整农业结构、推进土地综合整治、强化生态建设与环境保护,大力发展特色鲜明的现代农业,打造南京市农业主导产业配套生产基地,该土地利用类型在土地利用格局中占据绝对数量,且竞争力强。
2.3 南京市土地利用结构动态演变驱动因素分析
基于系统论基本原理[30],土地本身就是一个复杂系统,受自然、社会和经济要素共同作用。而土地利用结构动态演变就是系统与要素、结构与功能等共同作用下土地利用变化状况,是区域土地资源禀赋、经济发展水平、人口增长、产业结构布局、土地管理政策等要素综合作用的结果[10,31]。通过分析系统中各要素之间的相互关系及其规律,能够有效把握区域土地利用结构动态演变影响因素。
2.3.1 模型设定与指标选取
本文运用经济计量分析方法探究影响南京市土地利用结构时空格局演变规律的主要因素。经济计量模型形式如下:
Lusij=F(Lreij,Edlij,Pgij,Isaij,Lmpij)(12)
式中:Lusij(land use status)表示南京市第i年第j区土地利用变化状况,为被解释变量,基于已有研究启示[10,32],以土地利用结构信息熵衡量。所用解释变量说明如下:Lreij(Land resource endowment)表示第i年第j区土地资源禀赋状况,以区域年末耕地数量(hm2)衡量; Edlij(Economic development level)表示第i年第j区经济发展状况,以人均GDP(元/人)衡量; Pgij(Population growth)表示第i年第j区人口变化状况,以人口自然增长率(‰)衡量; Isaij(Industry structure adjustment)表示第i年第j区产业结构布局与调整状况,用第三产业占比(%)衡量; Lmpij(Land management policy)表示土地管理政策:2004年我国开始实行土地垂直管理体制,强化土地资源管理,落实最严格的耕地保护制度,同年4月,江苏省第十届人大常委第九次会议对《关于修改〈江苏省土地管理条例〉的决定》进行第二次修正; 2006年南京市调整并完善了《南京市土地利用总体规划(2006—2020年)》; 2008年,为有效应对全球性的金融危机,各项土地政策广泛的应用于宏观调控[11]; 2010年中共南京市委南京市人民政府出台《关于加快推进全域统筹建设城乡一体化发展的新南京行动纲要》,加强土地整治,集约节约利用盘活土地资源; 为响应“纲要”精神,2011年南京市制定了《关于规范推进农村土地综合整治工程的实施意见》; 2012—2014年南京市连续出台有关耕地保护、建设用地节约集约利用、违法用地监管等一系列政策制度; 2015年南京市实施了《南京市耕地保护补贴暂行办法》; 2016年作为“十三五”开局之年,其未来五年的目标任务在于“优化完善土地开发利用格局,逐步落实区域空间协调性发展”[33],因此,本文依据社会发展阶段,大致将2005—2008年赋值为1,2009—2011年赋值为2,2012—2015年赋值为3,2016年赋值为4。综上所述,经济计量模型可进一步表示为:
Lusij=α0+α1Lreij+α2Edlij+α3Pgij+
α4Isaij+α5Lmpij+εij(13)
式中:α0表示常数项; α1,α2,…,α5表示解释变量系数; εij表示误差项。
2.3.2 模型估计结果分析
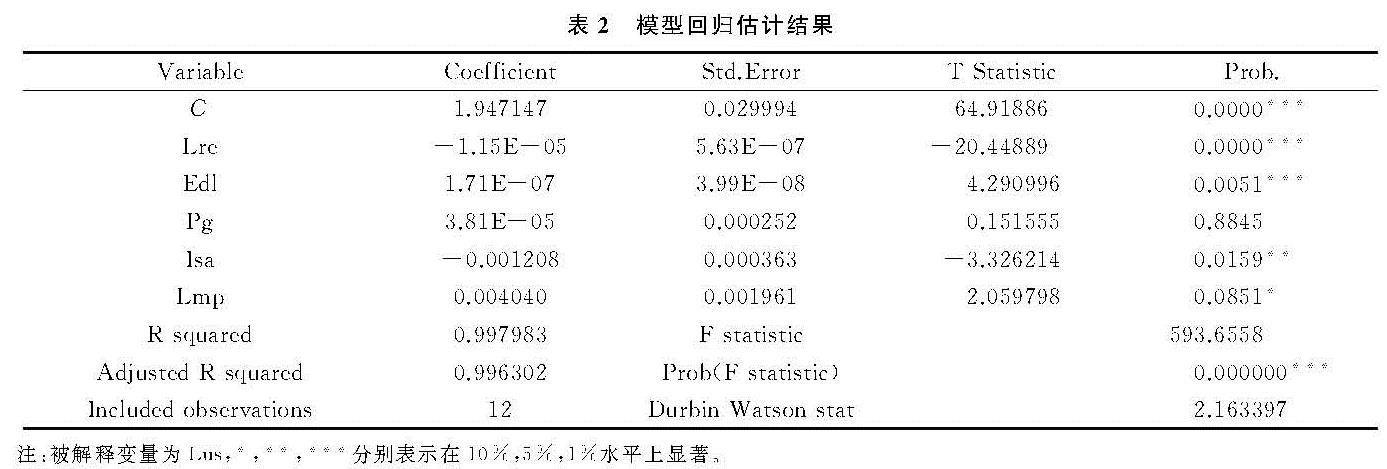
基于2005—2016年南京市11个区基础数据,借助Eviews 6.0软件,以南京市11个区土地利用结构信息熵Lus为被解释变量进行了回归分析,模型回归估计结果见表2。
表2模型估计结果中,从整体显著性来看,F值为593.66且p值为0.000,拒绝模型整体解释变量系数为零的原假设,表明模型整体拟合良好; 从拟合度来看,R2和调整R2均在99%,表明模型整体拟合度好; 从拟合残差序列相关性来看,D-W值为2.1,表明判断回归残差不存在序列自相关。因此,回归模型是有效的。从回归结果来看,土地资源禀赋、经济发展水平、产业结构和土地管理政策因素通过检验,对南京市土地利用结构变化具有显著影响,而人口因素未通过检验,但从其系数来看,属正相关关系,表明人口因素对南京市土地利用结构变化具有直接效应,与相关研究结论基本一致[34-35]。具体分析如下:
(1)在1%显著水平下,土地资源禀赋对南京市土地利用具有负相关,经济发展水平与其存在高度正相关,对该市土地利用结构变化具有较大拉动力。这是由于土地是一切生产生活的载体,经济发展水平提升必定导致区域建设用地需求增加,特别是随着城镇化与工业化的推进,促使基础设施建设等服务性用地刚性需求不断增加,占用大量土地(特别是耕地占用),导致区域内部土地资源结构发生变化。
(2)产业结构调整在5%水平上显著,与南京市土地利用具有显著负相关,表明第三产业占地区GDP比重越大,该区域土地利用结构调整内在驱动力就越大。这是由于产业结构调整会促使土地资源在部门之间的配置发生变化,同时由于土地与其他要素的配置关系在不同产业中存在一定差异,主导型产业转移必定推动着建设用地扩展,直接造成区域土地利用结构变化。
(3)土地管理政策在10%水平上显著,且估计系数为正,表明其对南京市土地利用方式、结构调整等具有正相关。面对一系列土地保护问题,南京市近年来连续出台了节地提效保发展、用地秩序监管、耕地与基本农田保护等管理政策,重点发挥土地资源保障功能,挖掘存量土地潜力,盘活闲置土地,加大土地生态保护投入与治理等,使得该市节地提效系列工作取得初步成效,在一定程度上有效地引导了该市土地资源合理利用与保护。