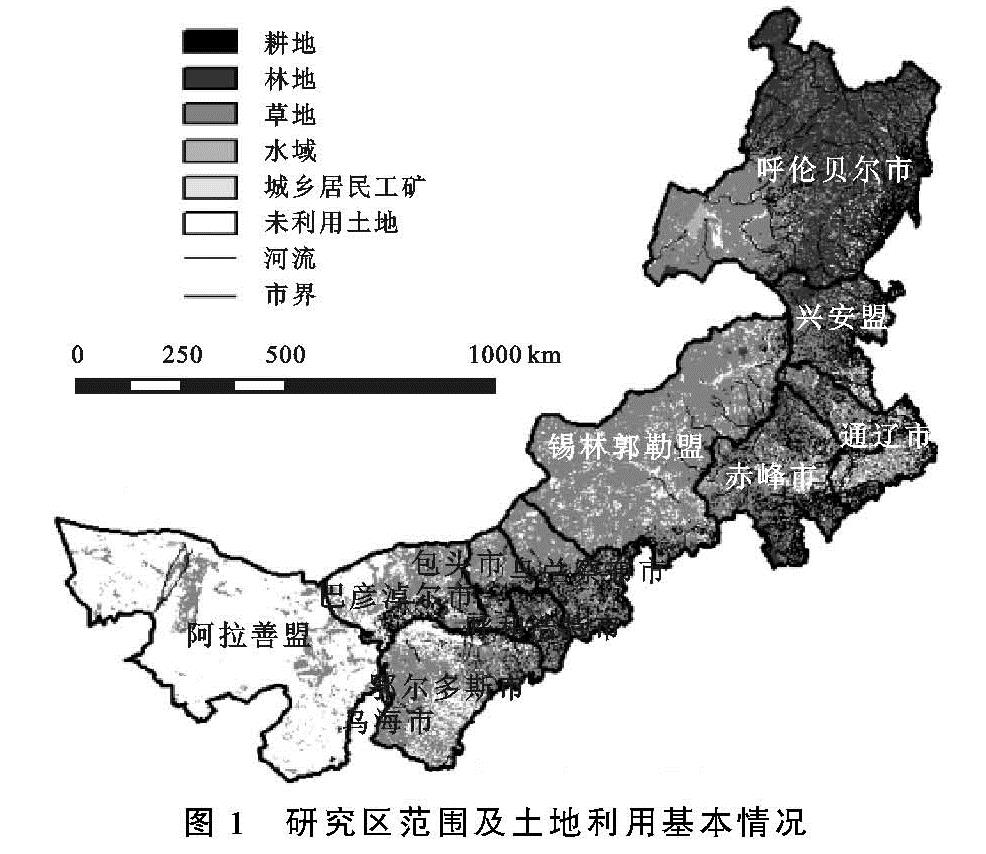
1.3.1 沙漠化脆弱性评估指标体系
VSD脆弱性评价框架将脆弱性分解为暴露性、敏感性和适应能力3个维度,暴露度包含干旱、人类活动等指标,敏感性包含植被、土壤、经济等因素,适应能力包含技术、经济等指标[9,15]。本文参考VSD脆弱性评价框架逐级递进、细化评价指标和数据,结合土地沙漠化的影响因素以及研究区实际情况,构建沙漠化脆弱性评估指标体系。基于前人研究以及专家知识,利用层次分析法,按照目标层、准则层和指标层建立层次结构,构建判断矩阵评定各层次中各有关因素相对重要性,进行层次单排序来确定各因素重要性次序的权重值,利用ArcGIS栅格计算器对各项指标进行加权求和得到各维度的空间分布图层,根据3个维度的关系(公式1)计算得到沙漠化脆弱性评估结果。
V=E+S-A(1)
式中:V为脆弱性; E为暴露度; S为敏感性; A为适应能力。
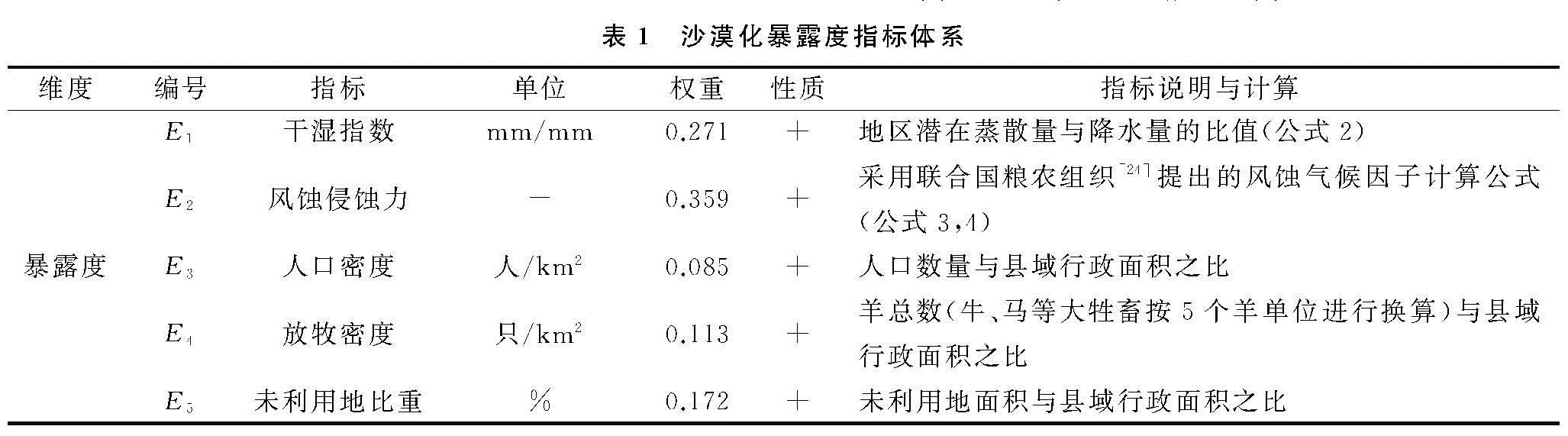
沙漠化暴露度是沙漠化系统暴露于外界压力或风险干扰与胁迫的程度,主要指气候变量及人类活动的干扰[11,23],包括干湿指数、风蚀气候侵蚀力、人口密度、放牧密度和未利用地比重5个指标(表1),均与沙漠化暴露度呈正相关,即暴露度随着各指标数值增加而升高。干湿指数综合了降雨、气温、辐射等多个气候要素,是表征一个地区干湿程度及对植被生长影响的重要指标,风蚀气候侵蚀力是影响土地沙漠化的重要外部营力[24],二者分别从地表干湿条件和风蚀程度表征土地沙漠化暴露度高低; 内蒙古地区农村人口比重较高,种植业和畜牧业是其主要的经营活动,人口的增多和畜牧量的增加会加剧土地退化,因此用人口密度和放牧密度代表人类活动对土地沙漠化暴露度的影响; 未利用土地比重是在自然环境的限制下,人类活动未开发利用的土地数量,未利用土地比重越高土地沙漠化暴露度越高。
E1=ET0/P(2)
E2=1/(100)∑12i=1u^-3(ET0i-Pi)/(ET0i))d(3)
ET0=0.19(20+T)2(1-r)(4)
式中:E1为干湿指数(mm/mm); ET0为最大潜在蒸散(mm); P为降雨量(mm); E2为风蚀气候侵蚀力(无单位); �Symbol`A@�u为2 m高处的月均风速(m/s); d为月天数; T为月平均气温; r为月平均相对湿度。
沙漠化敏感性是指外界条件变化对系统的格局、过程和功能的影响程度[9],包括植被覆盖度、土壤沙粒含量、粮食单产、单位面积水资源量、人均GDP和农村人口比重6个指标(表2)。植被覆盖度作为反映地表信息的重要参数,是影响土地荒漠化直接有效的指标,植被覆盖度越高沙漠化敏感性越低; 土壤沙粒含量和单位面积粮食产量代表了土壤质地和土壤肥力,作为代表土壤退化的敏感性指标,土壤沙粒含量越高、单位面积粮食产量越低沙漠化敏感性越高; 单位面积水资源量作为衡量某一地区的水量自我供给能力,不仅仅包括降水量还包括水库、江河湖泊和地下水,单位面积水资源量越高沙漠化敏感性越低; 内蒙古地区人均GDP和农村人口比重是影响沙漠化敏感性的经济因素,人均GDP越高、农村人口比重越低沙漠化敏感性越低。
S1=(NDVI-NDVImin)/(NDVImax-NDVImin)(5)
式中:S1为植被覆盖度(%); NDVImax和NDVImin分别为区域内最大和最小的NDVI值。
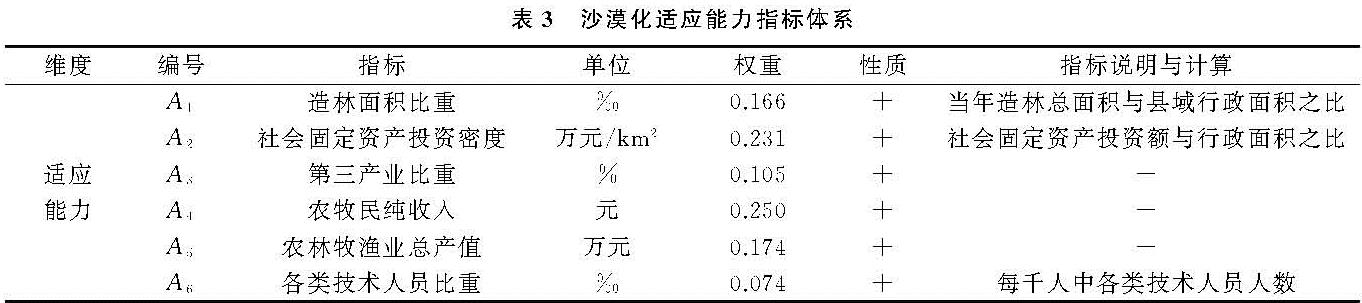
沙漠化适应能力是指沙漠系统适应气候变率和极端气候事件时减轻潜在损失、利用机会或应付气候变化的能力,是系统对变化的环境做出的调整[9,17],主要受社会经济因素影响,包括当年造林面积占总面积比重[26]、社会固定资产投资密度、第三产业比重、农牧民人均可支配收入、农林牧渔业总产值和各类技术人员比重6个指标(表3),各指标数值越高沙漠化适应能力越强。
1.3.2 数据处理
将社会经济数据的各指标数据赋值到以县为单位的矢量图中进行空间化,然后再根据不同的指标字段值生成对应的栅格数据层。由于评价指标类型多样,单位不一,需要对各项指标数据进行标准化统一处理,本文采用常用的min—max标准化(min—max normalization)方法(公式6,7)对数据进行无量纲化处理,在沙漠化脆弱性评价体系中,有些指标与维度呈正效应(暴露度、敏感性或适应能力随着相应指标数值的增大而升高),有些呈负效应(暴露度、敏感性或适应能力随着相应指标数值的增大而降低),根据各指标对相应维度的不同影响区别对待,最终将各指标数据整理为具有空间属性的归一化栅格数据。以2000—2015年脆弱性指数的均值的自然间断点为标准,对研究区沙漠化脆弱性进行等级划分,由低到高分为不脆弱、较低脆弱、等脆弱、较高脆弱和高脆弱(表4)。
正效应的指标处理方法为:
Xij=(xij-minxij)/(maxxij-minxij)(6)
负效应的指标处理方法为:
Xij=(maxxij-xij)/(maxxij-minxij)(7)
式中:Xij为标准化数据; xij为第i个评价对象的第j项评价指标; maxxij和minxij分别为第j项评价指标的最大值和最小值。经处理后的Xij∈[0,1]; Xij越趋于1,说明其对相对应维度的贡献越大; 反之,则越小。
1.3.3 分析方法
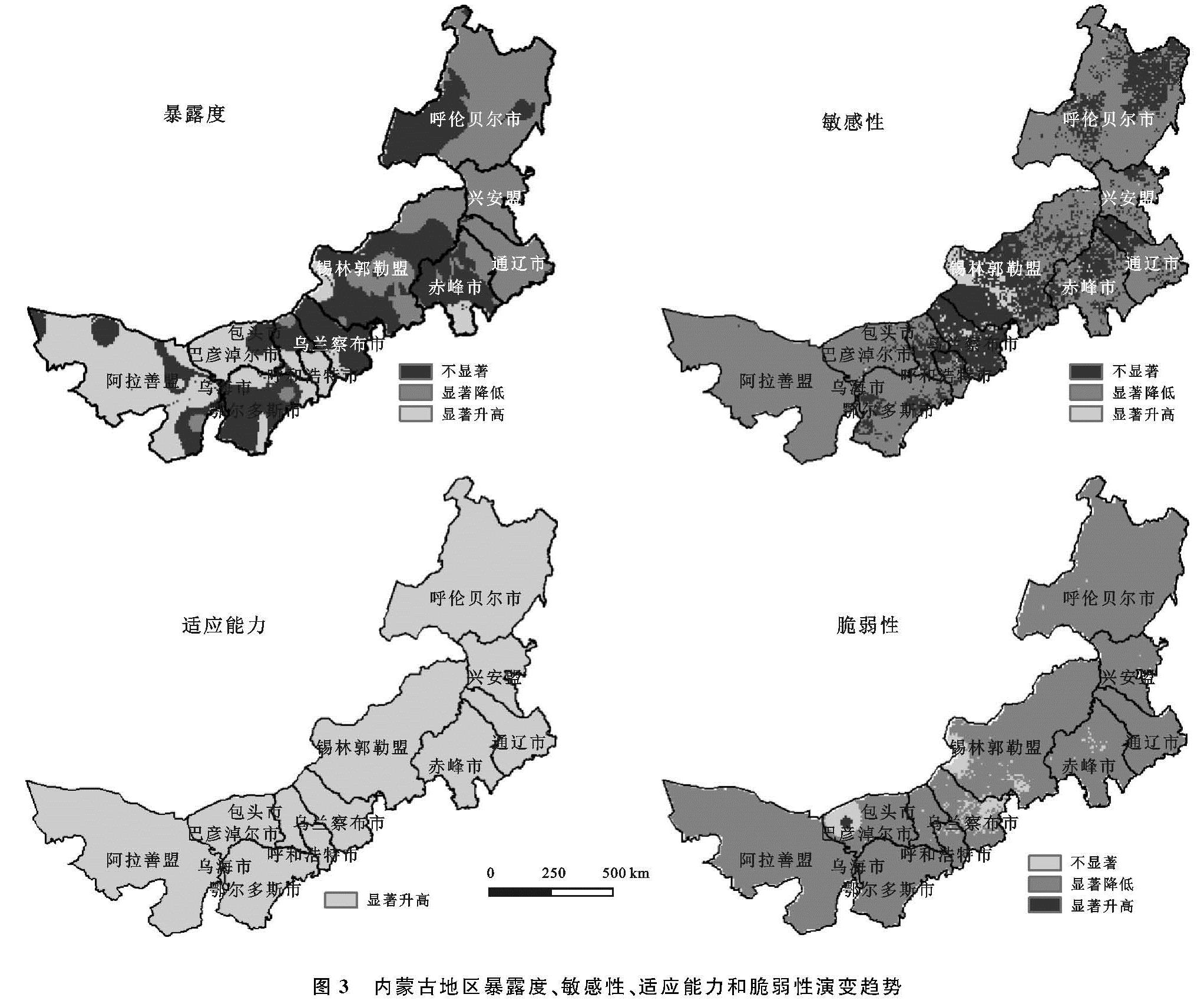
利用线性回归模型分析栅格尺度上的内蒙古地区2000—2015年土地沙漠化脆弱性、暴露度、敏感性和适应能力的年际变化趋势,并通过t检验法(p<0.05)对脆弱性以及构成脆弱性的3个维度进行显著性检验,判断其是否发生显著变化,来确定研究区沙漠化脆弱性演变趋势。为了进一步识别影响沙漠化脆弱性的关键因素,使用相关性系数分析各指标与沙漠化脆弱性评估结果的相关性,相关性系数绝对值越大则此指标对脆弱性结果影响越明显。若相关性系数大于0则表示正相关,此指标对脆弱性指数呈正向影响; 若相关性系数小于0表示负相关,此指标对脆弱性指数呈反向影响。相关性系数绝对值大于0.5时,指标y与x具有强相关关系。