资助项目:四川省科技厅项目”川西折多山高寒生态脆弱区植被恢复与重建技术研究”(2015FZ0022)
第一作者:苟天雄(1988—),男,四川剑阁人,工程师,硕士,主要从事植物学及生态恢复的研究工作。E-mail:435633002@qq.com 通信作者:刘韩(1983—),女,四川金堂人,工程师,硕士,主要从事生态恢复及林木微生物的研究工作。E-mail:helenliuhan@163.com
(四川省甘孜州林业科学研究所, 四川 康定 626001)
(Ganzi Institute of Forestry Research, Kangding, Sichuan 626001, China)
soil aggregate; stability; soil organic carbon; altitude; High-Frigid Mountainous
为探究川西北高寒山地不同海拔高度土壤团聚体分布特征及其稳定性,通过野外调查采样和室内试验分析的方式,对四川西部折多山高寒山地6个海拔梯度土壤团聚体特征进行了研究。结果 表明:0—20 cm土层不同海拔>0.25 mm粒径的土壤中非水稳性团聚体含量占80%以上,水稳定性团聚体含量占70%以上; 0—60 cm土层>0.25 mm粒径的土壤非水稳定性团聚体总体上呈现随海拔上升而增加的趋势,而水稳定性团聚体则呈现出随海拔升高先逐渐减小后增大的趋势。不同海拔土壤团聚体中有机质主要分布在>0.25 mm粒级中,且呈现随海拔升高先增加而后降低的趋势,随土层深度加深而逐渐降低的趋势。平均质量直径(MWD)、几何平均直径(GMD)均呈现出随海拔降低而逐渐减小的趋势,分形维数(D)则呈现增大的趋势,>20 cm土层规律不明显。表明川西高寒山地表层土壤团粒结构稳定性较好,防止土壤退化应是该区生态保护的重点。
In order to research the effect of altitude on the characteristics of soil aggregate and its stability in High-Frigid Mountainous region, based on field investigation and experimental measurement, we determined soil aggregate along altitude gradient. The results showed that the content of >0.25 mm air-dried aggregate was greater than 80%, the content of water stability aggregate was greater than 70%; the content of >0.25 mm air-dried aggregate in 0—60 cm soil layer increased with increase of altitude, and the content of soil water stability aggregate decreased at first and then increased with increase of latitude; the organic matter content of >0.25 mm aggregate was highest, it increased at first and then decreased with increase of latitude, and decreased with increase of soil depth; mean weight diameter and geometric mean diameter decreased with decrease of altitude, while fractal dimensionality in 0—20 cm soil layer showed the increasing trend, but the pattern wasn't obvious in >20 cm soil layer. These results indicated that the surface soil structure stability was better in the alpine mountain of western Sichuan, and prevention of soil degradation should be the focus of ecological protection in this area.
土壤团聚体作为土壤结构的基本组成单元,不仅综合了土壤中各种不同形状、大小、孔隙度和水稳性的团聚体,而且是土壤中养分的载体和微生物的生存环境[1]。同时土壤团聚体的粒径分布不仅反映土壤结构状况,而且影响着土壤的通气、抗蚀、渗水性等,与植被类型、气候条件等外部因子有重大联系,是评价土壤肥力和抗蚀性的重要指标[2-4]。此外>0.25 mm水稳性团聚体含量(R0.25)、平均质量直径(MWD)、几何平均直径(GMD)及分形维数(D)常用来描述团聚体的数量和分布状况,并作为土壤结构的稳定性和抗侵蚀能力的评价指标[5]。因此,通过研究土壤团聚体的分布特征,对于改善土壤肥力、增强土壤生产力、降低土壤可侵蚀性等具有重要意义。
近年来,国内外学者相继开展了关于土壤团聚体及其分布特征的研究,主要集中在不同森林植被类型、不同植被恢复年限以及不同林分发育阶段等对土壤团聚体分布及其稳定性的影响。赵友朋等[6]对凤阳山主要林分类型土壤团聚体及其稳定性的研究表明4 种林分土壤水稳定性大团聚体(WSA)(≥0.25 mm)含量均在90%以上。土壤水稳定性大团聚体含量及平均质量直径(MWD)和几何平均直径(GMD)均以杉木林的最大,竹林的最小。王小红等[7]研究了格氏栲天然林转化为人工林后的土壤团聚体有机碳的分布,发现天然林转换成人工林会导致土壤大团聚体数量减少,团聚体稳定性下降。庄正等[8]对不同发育阶段杉木人工林土壤团聚体分布特征及其稳定性研究表明各发育阶段杉木人工林土壤团聚体以>0.25 mm大团聚体为主,比例皆达80%以上,且中龄林和成熟林比例在各土层中均高于幼龄林。江仁涛等研究了川西北高寒草地退化对土壤团聚体组成及稳定性的影响[9]。但对于高海拔山地生态系统土壤团聚体分布特征及其稳定性的研究少见报道。川西高寒山地海拔较高,生态环境十分脆弱,对环境及气候变化尤为敏感。近年来随着人口增长和放牧强度的增加,对植被、土壤和生态系统过程干扰尤为强烈。尤其是高海拔地区冻融作用使土壤容重减小、孔隙度增大、团聚体水稳性减小[3],从而使土壤结构改变,稳定性降低,进而对土壤肥力及生态环境的屏障作用产生重大影响。因此,对川西北高寒山地不同海拔土壤团聚体分布特征及其稳定性进行研究,探讨海拔梯度及植被类型对土壤团聚体的粒径分布、组成和稳定水平,为科学评价高寒山地生态系统土壤结构及应对气候变化提供参考依据。
研究区位于四川省甘孜州折多山西部(30°00'—30°08'N,101°44'—101°51'E),折多山为大雪山一脉,属于青藏高原东缘,最高海拔4 962 m,垭口海拔4 298 m。研究区气候类型为亚寒带季风气候与高原大陆性气候交汇,气候温和偏寒,年日照2 000~2 500 h以上,年平均降水量1 600 mm,年均温8℃以下,冬季漫长,无明显夏季。主要土壤种类为高山暗棕壤和高山灌丛草甸土,植被垂直分布带由云冷杉针叶林过渡到海拔为3 800 m的高山林线再到4 000~4 200 m的高山灌丛草甸。
2016年8月在康定县折多山东坡进行土壤样品的采集,根据当地林线海拔约在3 800 m的实际情况,样地设置以3 800 m林线上下每隔200 m各设两个海拔梯度,即为3 400 m,3 600 m,3 800 m,4 000 m,4 200 m共5个海拔梯度。每个海拔梯度根据小地型植被的差异各设置3个20*20 m的标准样地(表1),并用五点采样法分剖面深度为0—20 cm,20—40 cm,>40 cm采集样品,同时用塑料盒采集原状土做团聚体分析及不同粒径风干团聚体做有机质含量分析。
根据中华人民共和国林业行业标准(LY/T-1999)测定相关指标[10]。土壤容重采用环刀法测定; 土壤团聚体分为水稳性团聚体和非水稳性团聚体,非水稳性团聚体用干筛法,水稳性团聚体的分级采用湿筛法测定。土壤有机质含量重铬酸钾外加热法测定。
团聚体平均质量直径(MWD):
MWD=(∑ni=1X^-i*Wi)/(∑nr=1Wr)(1)
团聚体几何平均直径(GMD):
GWD=exp[(∑ni=1Wi*lgX^-i)/(∑nr=1Wr)](2)
土壤分形维数(D):

式中:X^-i为任一粒级范围内团聚体的平均直径(mm); Wr为供试土壤总质量; Wi为对应于X^-i的团聚体质量;
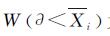
为小于X^-i的积累土粒质量; Xmax为最大粒级平均直径(mm),用线性回归的方法将

设置为纵坐标、lg[(X^-i)/(Xmax)]为横坐标作图,所求得该线性方程的斜率就是3-D,再通过计算就求得土壤分形维数(D)。
采用Excel软件对试验数据进行整理归纳,采用SPSS 20.0软件对各处理的数据进行方差分析和显著性检验。
团聚体作为组成土壤的重要部分,通过稳定土壤的结构而降低其水土流失,从而起到水土保持的作用。土壤中不同粒级大小聚体所占百分比,可表明团聚体的机械稳定性。由表2可以看出:各海拔土壤非水稳性团聚体0—60 cm土层各粒径含量大小为(>2 mm)>(2~1 mm)>(1~0.5 mm)>(<0.25 mm)>(0.5~0.25 mm),其中>2 mm 非水稳性团聚体含量最多,0.5~0.25 mm含量最小。不同海拔梯度土壤中,0—60 cm土壤>2 mm非水稳性团聚体含量均值大小顺序为:4 200 m(52.3%)>3 600 m(50.23%)>3 400 m(42.38%)>4 000 m(42.21%)>3 800 m(41.06%),且随海拔梯度变化规律不明显,呈现出随海拔升高逐渐减小而又后增大的趋势。其中海拔4 200 m的土壤>2 mm非水稳性团聚体所占比例最高,而海拔3 800 m最低。但>2 mm 非水稳性团聚体在0—20 cm土层范围中,所占比例大小依次为:4 200 m(60.42%)>3 800 m(55.74%)>3 600 m(53.07%)>4 000 m(49.37%)>3 400 m(38.87%,),除4 000 m外呈现出随海拔增高而逐渐上升的趋势,表明0—20 cm土层中所含大粒径团聚体较多,且随着土层的加深而降低,但其余粒径规律则不明显。一般将>0.25 mm的团聚体称为土壤团粒结构体,是维持土壤结构稳定的基础,其含量越高,土壤结构的稳定性越大[7.8]。根据表2计算得到不同海拔土壤>0.25 mm 粒径的非水稳性团聚体含量组成大小为:4 200 m(87.06%)>3 600 m(86.61%)>3 800 m(86.08%)>3 400 m(81.70%)>4 000 m(80.58%),其中最大是海拔4 200 m的土壤,最小的为海拔4 000 m的土壤,差异不明显,总体上呈现随海拔上升而增加的趋势,4 000 m处较低可能与该海拔放牧强度较高,植被破坏相对于其他海拔严重有关。
土壤团聚体稳定性尤其是水稳性团聚体是反映土壤结构的重要指标,与土壤的抗侵蚀能力以及环境质量有着密切的关系[11]。由表3可以看出,不同海拔的土壤>2 mm的水稳性团聚体在各粒径中比例最高,均值大小顺序为:3 600 m(35.34%)>3 800 m(34.19%)>4 200 m(33.88%)>4 000 m(31.06%)>3 400 m(30.35%),呈现出随海拔升高先降低后增加的趋势,但差异不显著。从0—20 cm土层看,>2 mm的水稳性团聚除4 000 m外呈现出随海拔增高而逐渐增加的趋势,表明0—20 cm土层中所含水稳性大粒径团聚体比例较高,且随着土层的加深而降低,其余粒径规律则不明显。>0.25 mm 粒径的水稳性团聚体含量组成大小为:3 800 m(80.18%)>3 600 m(78.67%)>4 200 m(75.01%)>3 400 m(74.14)>4 000 m(72.03%)。>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤水稳性团聚体含并随海拔升高呈现先升高后降低趋势,在3 800 m林线处最高,说明海拔3 800 m林线附近土壤的抗水力侵蚀性相对较好,低于和高于林线的土壤水稳定性相对较差。不同海拔土壤<0.25 mm的水稳性团聚体含量则呈现相反的规律,均值大小顺序为:4 000 m(27.97%)>3 400 m(25.85%)>4 200 m(25.00%)>3 600 m(21.34%)>3 800 m(19.82%)。另外,同一粒径同一土层不同海拔差异性不显著。
土壤腐殖质是土壤团聚体的主要胶结剂,同时也是土壤有机质保存的重要场所,对土壤的肥力和结构特征尤其在提高土壤团聚体稳定性方面具有重要的意义。由表4可以看出,从整体来看,有机质含量主要集中在>0.25 mm粒径的大团聚体中,占比在80%左右,含量大小顺序为:3 800 m(361.25 g/kg)>4 200 m(315.01 g/kg)>3 600 m(276.19 g/kg)>4 000 m(269.14 g/kg)>3 400 m(265.05 g/kg),以3 800 m处最高,随海拔升高呈现先增加而后降低的趋势,随着土层深度加深而呈现出逐渐降低的趋势。<0.25 mm粒径的团聚体则规律不明显。在0—20 cm土层中,各粒径非水稳性团聚体中有机质含量均表现3 800 m>4 200 m>3 600 m>4 000 m>3 400 m,即呈现出较为明显的随海拔升高先增加而后降低的趋势、20—40,40—60 cm的变化规律不明显。>0.25 mm粒径的团聚体中有机质相同海拔土壤同一层中,随着土壤团聚体粒径的变化其有机质含量变化没有明显规律性且差异不明显。
团聚体平均质量直径(MWD)、几何平均直径(GMD)和分形维数(D)是用于评价团聚体稳定性十分重要的指标。粒径大的团聚体组成比例越高,土壤MWD就越大,土壤团聚体越稳定[12]。由表5、表6可以看出,0—20 cm土层中,土壤非水稳性团聚体和水稳性团聚体在5种不同海拔土壤MWD最大的是海拔4 000 m的土壤,最小的是海拔3 400 m的土壤; GMD最大的是海拔4 200 m的土壤,海拔3 800 m的土壤次之,最小的是海拔3 400 m的土壤; 总体上看,0—20 cm土层各海拔高度土壤非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD都呈现随海拔高度的升高变化趋势,20—40,40—60 cm土层规律不明显,但有随海拔高度增加MWD,GMD则都呈现出与0—20 cm相反的变化规律,即呈现减小的趋势。不同海拔土壤随土层深度的增加,非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD均呈现下降的趋势。
土壤团粒结构的分形维数(D)是评价土壤团聚体稳定性的一项指标,团粒结构分形维数越小,土壤的结构和稳定性越好,抗蚀能力越强。表5、表6可以看出,0—20 cm土层中非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体分形维数D值最小值是4 200 m,3 800 m次之,3 400 m值最大,但整体呈现随海拔升高增大的趋势,而20—40,40—60 cm土层规律不明显。各海拔高度土壤分形维数D亦表现出随土层的加深而增大的趋势,5种不同海拔土壤团聚体稳定性在0—20 cm土层团聚度高于下层。在不同海拔梯度0—20 cm土层土壤中,海拔4 200 m和3 800 m土壤的团聚体稳定性较高,土壤结构较稳定,在雨水冲刷下不容易被分散破碎,抗蚀性较好; 而海拔3 400 m土壤的MWD,GMD相对较低,D值较高,稳定性和易侵蚀性也相对较弱。
土壤团聚体组成以及其稳定性是评估土壤结构稳定性的重要指标之一[12]。一般将>0.25 mm的团聚体称为土壤团粒结构体,是维持土壤结构稳定的基础,其含量越高,土壤结构的稳定性越大[6]。本研究发现在川西高寒山地不同海拔>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤中非水稳性团聚体含量和水稳性团聚体含量均较高,其中非水稳性团聚体含量各海拔均达到80%以上,最高达87.06%,水稳定性体含量占70%以上,最高达到80.18%,尤其是在0—20 cm土层中,>2 mm 粒径团聚体含量在各粒径中含量也最高,说明研究区川西高寒山地土壤团聚体稳定性高。这与大多数学者认为土壤中>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤中团聚体含量占比大,团聚体稳定性也就好的结论相符[11-19]。从分布规律来看,0—60 cm土层>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤非水稳定性团聚体均值总体上呈现随海拔上升而增加的趋势,而水稳定性团聚体则呈现出随海拔升高先逐渐减小后增大的趋势。说明海拔3 800 m林线附近土壤的抗水力侵蚀性相对较好,低于和高于林线的土壤水稳定性相对较差。表明土壤团聚体稳定性与植被类型密切相关,3 800 m林线是一个转折,林线以上海拔较高的灌丛草甸植被虽然风干团聚体较高,但其水稳性团聚体则相对较低,说明其更容易被破坏。因此,保护高山林线植被对高寒山地生态环境稳定及防止水土流失具有重要意义。
团聚体和有机碳的关系密切,土壤有机碳是团聚体形成的物质基础,土壤有机碳的分解转化受团聚体影响,从而影响到土壤肥力的发挥[7]。本研究发现不同海拔土壤团聚体有机质主要分布在>0.25 mm粒级中,这与江仁涛[17]、李柏桥[18]、苑亚茹等[20]学者的研究结果相同。从海拔梯度分布情况看,土壤团聚体有机质呈现随海拔升高呈现先增加而后降低的趋势,其中以3 800 m处最高,与>0.25 mm水稳定性团聚体分布规律类似,<0.25 mm粒径的团聚体则规律不明显。不同海拔、不同粒径的土壤有机质含量均随着土层深度加深而呈现出逐渐降低的趋势。本研究中,不同海拔各土层中土壤各粒径团聚体有机质含量表现为随着土层加深而减少的趋势。这与黄晓强等[19]北京山区典型人工林土壤团聚体研究和苑亚茹等[20]对东北黑土区的研究也表明随着土壤层次的加深,土壤有机碳含量均呈现了逐渐降低趋势的结果相同。从整体来看,各海拔高度的土壤中大团聚体有机质含量相对较高,据王淑平等[21]研究表明随着海拔高度增加水分适宜但温度较低,土壤微生物的活动受到抑制,有利于有机质的积累,所以海拔高度的变化影响土壤温度和土壤水分的变化,在这两种因素共同作用下,土壤中有机物含量随着海拔高度升高呈现先升高后降低趋势,这与本研究结果相似。
土壤团聚体平均质量直径(MWD)、几何平均直径(GMD)和分形维数(D),是用于评价团聚体稳定性十分重要的指标,常用来反映团粒结构的稳定性,可以表示团聚体颗粒大小和粒级分布情况[17]。MWD和GMD值越大,表明土壤大团聚体含量越高,土壤团聚程度越高,土壤结构更加稳定[9,22]。本研究中,0—20 cm土层各海拔高度土壤非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD都呈现随海拔高度的升高变化趋势,20—40,40—60 cm土层规律不明显。随土层深度的增加,非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD均呈现下降的趋势。赵友朋[6]、刘艳等[22]研究表明,同一林分中,随土层的加深,土壤水稳性大团聚体含量和稳定性均呈下降趋势,与本研究结果类似,不同海拔高度非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体分形维数(D)则与MWD,GMD呈现相反的规律性。本研究发现>0.25 mm水稳性团聚体含量与非水稳定性团聚体呈显著正相关,与团聚结构破坏率呈负相关,说明不同海拔高度土壤大团聚体含量越多,土壤团粒大小分布越均匀,团聚结构被破坏的程度就越低,土壤结构稳定性越强。
(1)不同海拔>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤中非水稳性团聚体含量占80%以上; 水稳定性体含量占70%以上,尤其是在0—20 cm土层中,>2 mm 粒径团聚体含量在各粒径中含量也最高,说明研究区川西高寒山地土壤团聚体稳定性高。从分布规律看,0—60 cm土层>0.25 mm 粒径的土壤非水稳定性团聚体总体上呈现随海拔上升而增加的趋势,而水稳定性团聚体则呈现出随海拔升高先逐渐减小后增大的趋势。
(2)从整体来看,有机质含量主要集中在>0.25 mm粒径的大团聚体中,占比在80%左右。以3 800 m处最高,随海拔升高呈现先增加而后降低的趋势,随着土层深度加深而呈现出逐渐降低的趋势。<0.25 mm粒径的团聚体则规律不明显。不同海拔、不同粒径的土壤有机质含量均随着土层深度加深而呈现出逐渐降低的趋势。
(3)0—20 cm土层各海拔高度土壤非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD都呈现随海拔高度的升高变化趋势,0—20 cm土层土壤不同海拔土壤随土层深度的增加,非水稳性团聚体与水稳性团聚体MWD,GMD均呈现出随海拔降低而逐渐减小的趋势,分形维数D则呈现增大的趋势。>20 cm土层规律不明显。研究发现在高寒山地土壤中>0.25 mm水稳性团聚体含量与非水稳定性团聚体呈显著正相关,与团聚结构破坏率呈负相关,表明表层土壤团粒结构稳定性较好,一旦破坏将对高寒山地生态系统带来严重后果,防止土壤退化应是该区生态保护的重点。