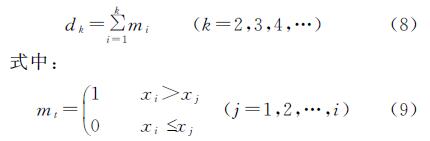2.1 数据来源与处理
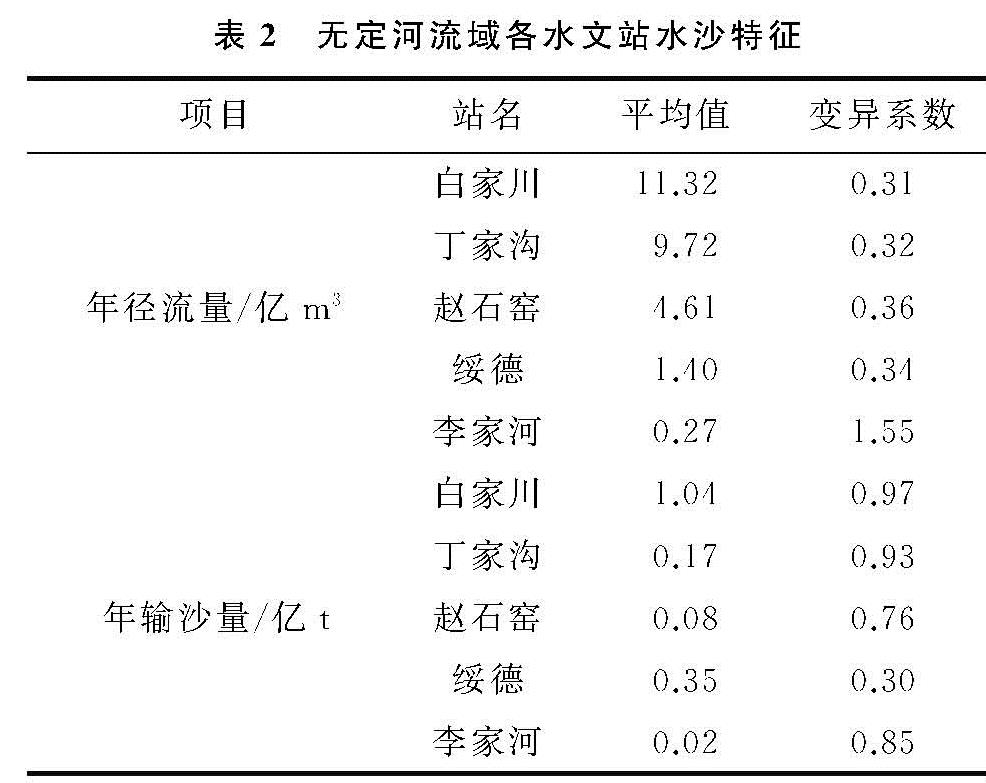
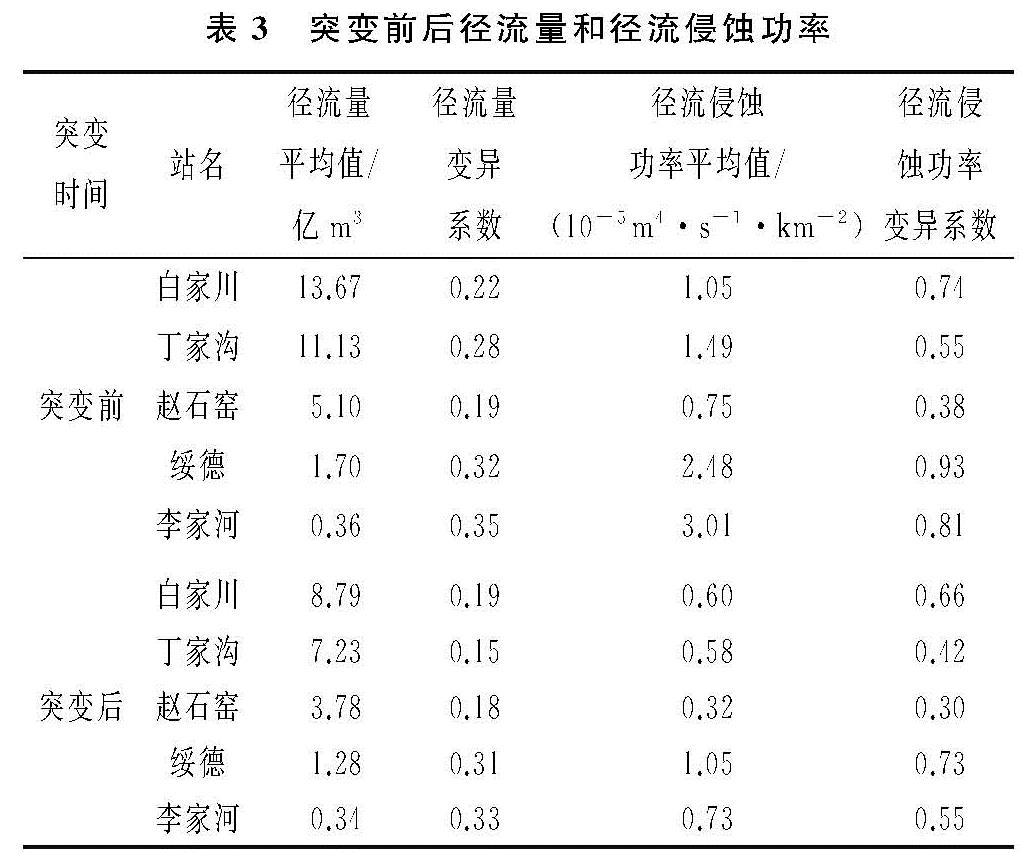
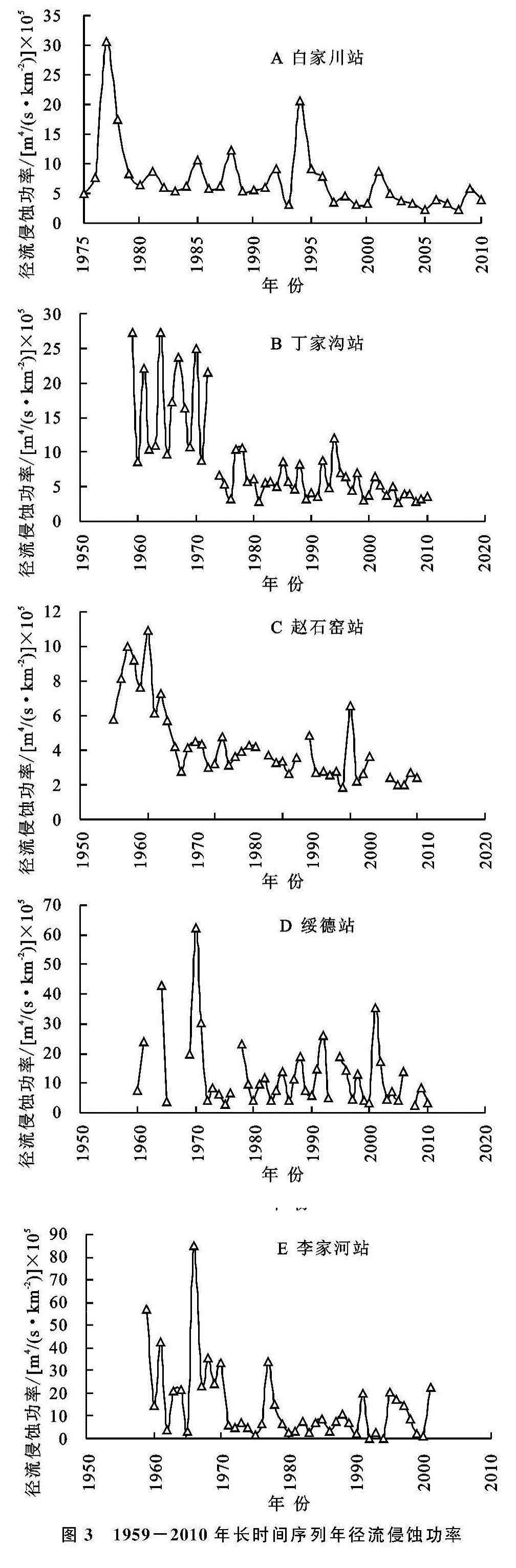
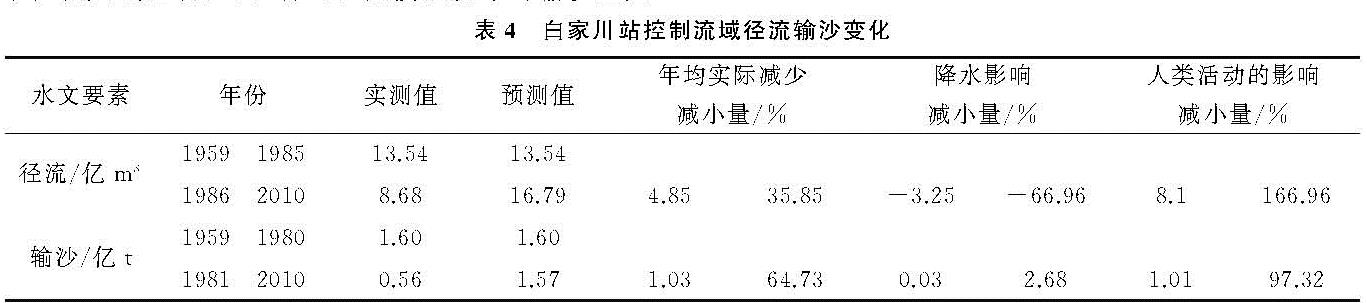
本文所用的水文资料来源于黄河水文年鉴中1956—2010年的水文资料,选取无定河流域5个代表水文测站李家河站、绥德站、赵石窑站、丁家沟站和白家川站(图1),各代表站分别控制小理河流域、大理河流域、无定河赵石窑站以上流域、无定河丁家沟站以上流域、无定河流域,控制流域面积分别为807 km2,3 893 km2,15 325 km2,23 422 km2,29 662 km2。
2.2 研究方法
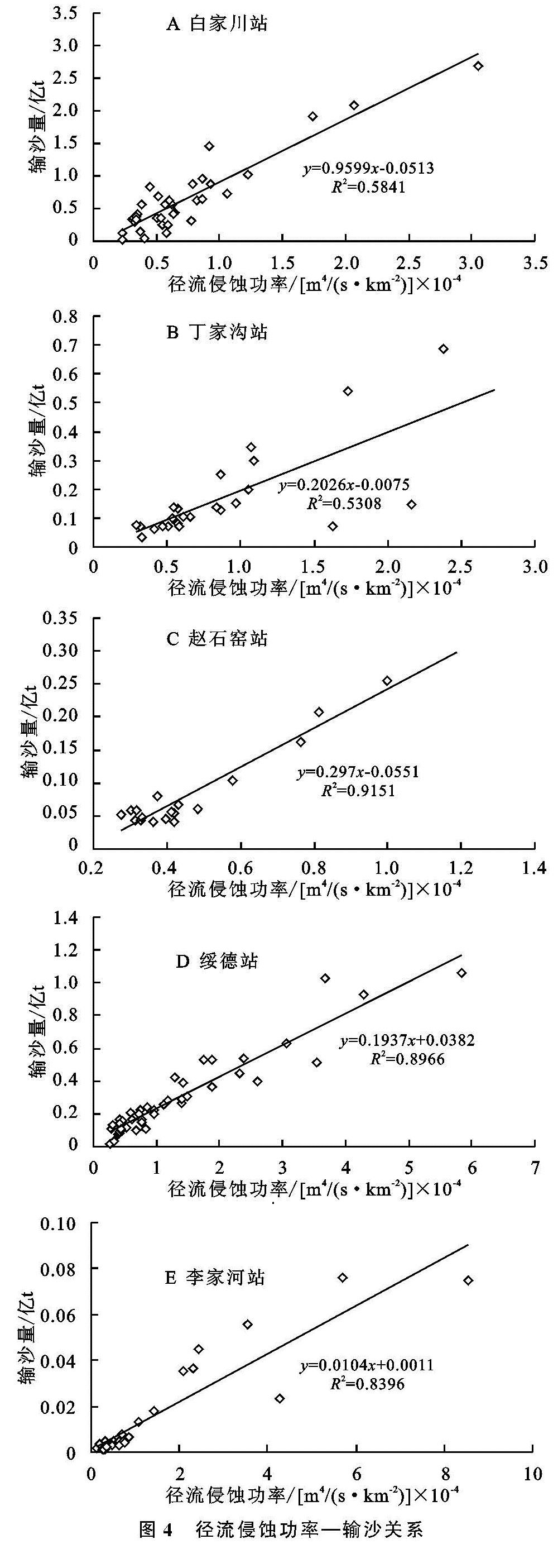
目前,在研究径流侵蚀方面主要有剪切力模型和侵蚀能量模型两大类[11-14],本文采用侵蚀能量模型中的径流侵蚀功率理论。
通过以下公式计算出径流侵蚀产沙的侵蚀动力指标:
E=Q'mH=W/A(Qm)/A=W/(A2)A'(Qm)/(A')
=(A')/(A2)WV=(A')/(ρgA2)ρgWV=(A')/(ρgA2)FV(1)
令Con=(A')/(ρgA2),则:
E=Con·F·V(2)
式中:W为径流总量(m3); A为流域面积(m2); Qm为洪峰流量(m3/s); A'为与Qm对应的流域出口断面的过水面积(m2); V为流域出口断面与Qm对应的平均流速(m/s); ρ为水的密度(kg/m3); g为重力加速度(m/s2); F为作用力(N)。
可以看出,指标E具有功率的量纲。本文将径流年内分配试作一次径流过程[15],通过使用径流侵蚀功率的计算公式,计算出年径流侵蚀功率,从年尺度上研究流域径流侵蚀功率的时空变化特征。
则以下式中:各项含义分别为:
Ea=Q'm·H(3)
式中:Ea为年径流侵蚀功率[m4/(s·km2)]; H为月平均径流深(m); Q'm为最大月平均流量模数[m3/(s·km2)],其大小等于最大月平均流量与流域面积的比值。
本文采用Mann-Kendall非参数秩次相关检验法[16]来进行水沙变化趋势分析。可构造统计量:

式中:
τ=(4∑ni=1pi)/(n(n-1))(5)
var(τ)=(2(2n+5))/(9n(n-1))(6)
统计量U称为Kendall秩次相关系数,当n增加时,U将很快收敛于标准正态分布。给定显著性水平α,其双尾检验临界值为Uα/2,当|U|α/2时,系列趋势不显著,资料一致性较好; 当|U|>Uα/2时,系列趋势显著,如U>0,系列呈上升趋势,如U<0,系列呈下降趋势。
线性回归法通过建立年径流序列yt与相应的时序t之间的线性回归方程来检验时间序列的线性变化趋势[17-18]。线性回归方程为:
yt=at+b(7)
式中:yt为实测序列; t为时序(t=1,2,…,n; n为序列长度); a为斜率,表征时间序列的平均趋势变化率; b为截距。
Mann-Kendall突变点诊断法被用于进行突变年份的检验。当Mann-Kendall法用于检验序列突变性时[19],需构造一个秩序列d:
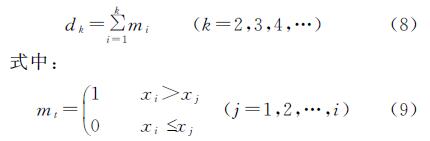
在时间序列随机独立的假定下,dk的均值和方差可由下边两个式子计算:
E(dk)=(k(k-1))/4(10)
var(dk)=(k(k-1)(2k+5))/(72)(11)
定义统计变量

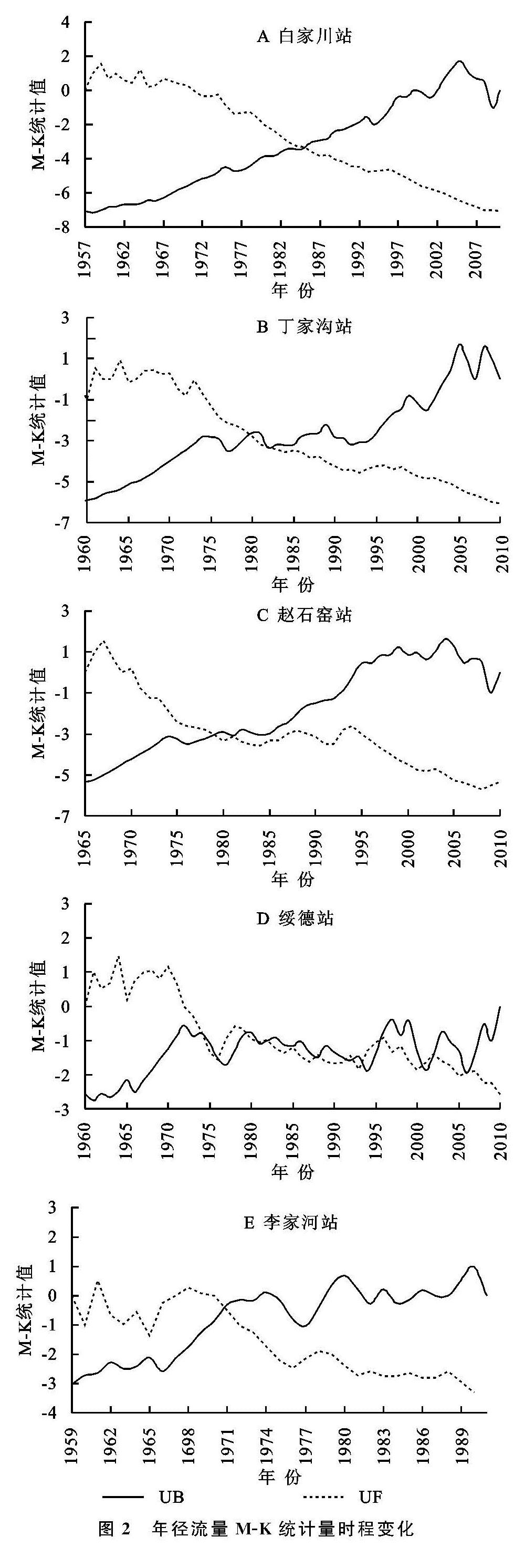
按时间序列逆序,再重复上述过程,同时使UBL=-UFK(L=n+1-k),由UFK绘制出曲线C1,由UBL绘制出曲线C2。若UFK或UBL的值超过临界直线,表明序列上升或者下降趋势显著。如果C1或C2出现交点,且交点在临界线之内,那么交点对应的时刻便是突变开始的时间。